In today’s world of ever-evolving technology, battery tester batteries power everything from our smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage systems. Ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of these batteries is crucial, and that’s where battery testers come into play. These handy devices provide valuable insights into the health and capacity of batteries, helping us make informed decisions about their usage and replacement.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of battery testers, exploring their types, working principles, applications, and the latest advancements in the field. We’ll also address some common questions and concerns frequently raised by users.
Types of Battery Testers
Battery testers come in a wide array of shapes and sizes, each designed to cater to specific battery types and applications. Here are some of the most common types:
Simple Multimeters: These versatile tools can measure voltage, current, and resistance, providing a basic assessment of battery health. While not as sophisticated as dedicated battery testers, they are readily available and affordable.
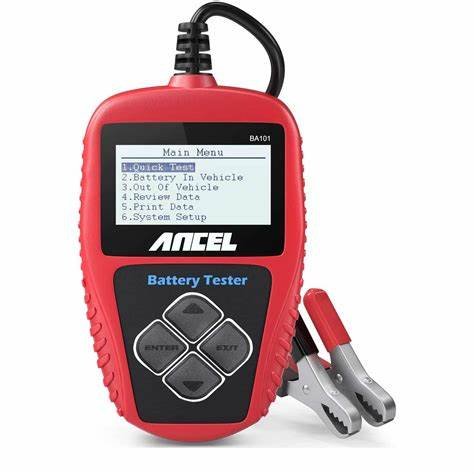
Dedicated Battery Testers: These devices are specifically designed for testing various battery types, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-metal hydride batteries. They often feature advanced capabilities such as load testing, internal resistance measurement, and state-of-health analysis.
Automotive Battery Testers: These testers are tailored for testing automotive batteries, providing crucial information about cranking amps, charging capacity, and overall battery health. They are essential for diagnosing battery-related issues in vehicles.
Industrial Battery Testers: These robust testers are used in industrial settings to evaluate the performance of large battery banks, such as those found in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and electric vehicles. They often incorporate advanced diagnostic features and data logging capabilities.
DIY Battery Testers: For hobbyists and enthusiasts, DIY battery testers offer a hands-on approach to understanding battery behavior. These simple circuits can be built using readily available components, providing a basic understanding of battery testing principles.
Working Principles of Battery Testers
The fundamental principle behind most battery testers is the measurement of various electrical parameters, including:
Voltage: The electromotive force generated by the battery, indicating its charge level.
Current: The flow of electrical charge, providing insights into the battery’s ability to deliver power.
Resistance: The opposition to the flow of current within the battery, influencing its internal losses and overall performance.
Capacity: The amount of electrical energy a battery can store, measured in ampere-hours (Ah).
State of Charge (SOC): The percentage of available capacity remaining in the battery.
State of Health (SOH): An overall assessment of the battery’s performance compared to its original specifications.
By analyzing these parameters, battery testers can accurately assess the battery’s health, identify potential issues, and predict its remaining lifespan.

Applications of Battery Testers
Battery testers find applications in a wide range of industries and everyday life:
Automotive Industry: Testing car batteries, ensuring optimal engine starting and preventing electrical system failures.
Industrial Applications: Monitoring the health of large battery banks in UPS systems, electric vehicles, and renewable energy installations.
Consumer Electronics: Testing rechargeable batteries in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices.
Hobbyists and DIY Enthusiasts: Building and testing custom battery packs for RC cars, drones, and other electronic projects.
Research and Development: Evaluating the performance of new battery technologies and materials.
Latest Advancements in Battery Testing Technology
The field of battery testing is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging to address the growing demand for high-performance and long-lasting batteries. Some of the latest advancements include:
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Techniques: These methods, such as impedance spectroscopy and acoustic emission testing, allow for the assessment of battery health without physically damaging the battery.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being used to analyze complex battery data, predict battery degradation, and optimize charging and discharging strategies.
Wireless Battery Monitoring Systems: These systems enable real-time monitoring of battery performance and health remotely, facilitating proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) Sensors: MEMS-based sensors are being integrated into battery packs to provide accurate and real-time measurements of various parameters, including temperature, voltage, and current.
Advanced Testing Techniques
While basic voltage and current measurements provide valuable insights, advanced battery testers employ sophisticated techniques to assess battery health more comprehensively:
Load Testing: This technique simulates a load on the battery, such as the starting current of a car engine, to evaluate its ability to deliver power under real-world conditions.
Internal Resistance Measurement: By measuring the internal resistance of the battery, testers can assess its overall health and predict its remaining lifespan.
Capacity Testing: These tests determine the actual capacity of the battery, comparing it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
State-of-Health (SOH) Analysis: SOH analysis provides an overall assessment of the battery’s performance, taking into account various factors such as voltage, current, resistance, and capacity.
Final Thoughts
Battery testers are indispensable tools for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of batteries across various applications. By providing valuable insights into battery health and capacity, these devices empower us to make informed decisions about battery usage, maintenance, and replacement. As battery technology continues to evolve, so too will battery testing techniques, paving the way for a future where batteries are more reliable, efficient, and sustainable.
FAQs
What is a battery tester and what does it do?
A battery tester is a device used to assess the health and performance of batteries. It measures various electrical parameters like voltage, current, resistance, and capacity to determine if a battery is fully charged, has sufficient power, and is in good working condition.
What types of batteries can be tested?
Battery testers can be designed for various battery types, including lead-acid batteries (commonly used in cars, trucks, and motorcycles), lithium-ion batteries (found in smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and power tools), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries (used in some older devices and hybrid vehicles), and alkaline batteries (common in everyday household items like remote controls and toys).
How do battery testers work?
Most basic testers measure voltage, which indicates the battery’s charge level. Advanced testers utilize more sophisticated methods like load testing (simulating a real-world demand on the battery to evaluate its ability to deliver power), internal resistance measurement (assessing the battery’s internal resistance, a key indicator of health), and capacity testing (determining the actual capacity of the battery).
To read more, Click Here











Leave a Reply